아파치 스쿱(Apache Sqoop)-RDB와 하둡(hadoop)을 연결해보자
업데이트:
아파치 스쿱(Apache Sqoop)이란?
참고링크
관련링크
하둡에 대해 알아보자
일을 하다보면 관계형데이터베이스(RDB)에서 하둡으로 테이블을 보내거나,
반대로 하둡에서 RDB로 테이블을 보내야 할 때가 있습니다.
아파치 스쿱은 RDB와 하둡 사이에서 둘 사이의 연결을 도와주는
명령 줄 인터페이스(Command-Line Interface) 애플리케이션 입니다.
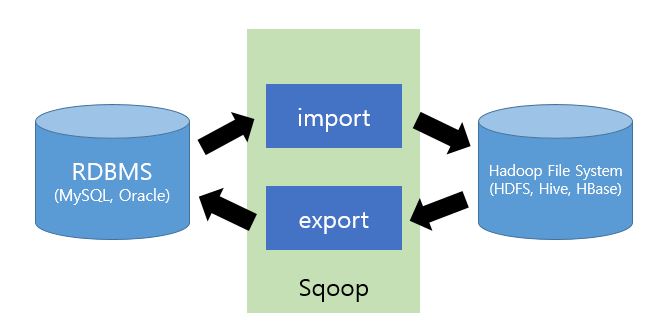
이런 형태로 스쿱이 RDB와 하둡의 중간에 위치한다고 볼 수 있습니다. 명령어는 크게 import와 export로 구성 되어있습니다.
- import : RDB -> HDFS (RDB에서 HDFS로 데이터를 가져옵니다.)
- export : HDFS -> RDB (HDFS에서 RDB로 데이터를 가져옵니다.)
import 예시
$ sqoop import --connect \"URL\" --username \"USERNAME\" --password \"PASSWORD\" --table \"QUERY\" --target-dir \"PATH\" --as-parquetfile --m 1
잘라서 가져오기
sql 문장을 실행했을때 나오는 데이터가 아주 큰 경우에는 잘라서 가져올 필요가 있습니다. 그럴때는 import 하는 sql문에 $CONDITIONS 를 포함해야 합니다. 프리스타일 sql문을 사용하는 경우(쌍따옴표 안에 sql문을 넣을 경우)에는 \$CONDITIONS 를 추가해야합니다. 또한 어느 열을 기준으로 자를지를 결정하는 –split-by 또한 포함해야 합니다.
Sqoop can also import the result set of an arbitrary SQL query. Instead of using the –table, –columns and –where arguments, you can specify a SQL statement with the –query argument.
When importing a free-form query, you must specify a destination directory with –target-dir.
If you want to import the results of a query in parallel, then each map task will need to execute a copy of the query, with results partitioned by bounding conditions inferred by Sqoop. Your query must include the token $CONDITIONS which each Sqoop process will replace with a unique condition expression. You must also select a splitting column with –split-by.
For example:
$ sqoop import \
--query 'SELECT a.*, b.* FROM a JOIN b on (a.id == b.id) WHERE $CONDITIONS' \
--split-by a.id --target-dir /user/foo/joinresults
Alternately, the query can be executed once and imported serially, by specifying a single map task with -m 1:
$ sqoop import \
--query 'SELECT a.*, b.* FROM a JOIN b on (a.id == b.id) WHERE $CONDITIONS' \
-m 1 --target-dir /user/foo/joinresults
